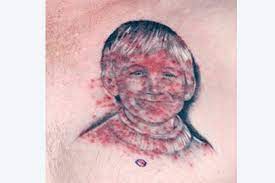
Normal Reactions of Getting Tattooed
Typical reactions after getting a tattoo include itching, swelling, and redness in the tattooed area. These reactions usually only affect the top layers of the skin around the tattoo. Scabs may form, but it is crucial not to pick at them to avoid infection and ink loss. The scabs should naturally flake off over time.
Allergies
Tattoo ink can sometimes cause redness and itching due to the body’s immune response to foreign substances in the skin. However, more severe symptoms may indicate an allergy. Allergies to tattoo pigments are uncommon, as most inks contain organic ingredients that vary in structure, making identification and testing challenging. Seek immediate medical assistance if you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or stomach ache. Doctors or dermatologists can examine your tattoo, prescribe antibiotics for infections, and remove affected areas if necessary. Allergy specialists can perform skin prick testing to check for tattoo ink allergies by placing patches of potential allergens on the skin for 24 hours.
Contact Dermatitis
Tattoo pigments can cause contact dermatitis, resulting in red, itchy skin with bumps or blisters. Contact dermatitis is not contagious and resolves itself once the source of the irritation is eliminated. If you have any adverse reactions after getting a tattoo, consult a medical professional. They can perform a physical exam, gather more information about your symptoms, and conduct allergy testing using diluted test allergens applied to your skin for 48 hours.
Infections
Tattooing can lead to various infections, most commonly bacterial. These infections are often caused by unclean equipment or ink or scratching or picking at the tattooed skin. Conditions can be life-threatening, spreading to other body parts and causing sepsis. See medical advice immediately if you experience symptoms like fever or red bumps around the tattoo.
Adverse Reactions to Tattoo Pigments
Allergic reactions to tattoo pigments can manifest as itchy, red, and flaky symptoms, appearing days, years, or decades after getting a tattoo. Certain cadmium sulfur dyes, such as yellow and red hues, can trigger these reactions. Antihistamine medications can help relieve symptoms like red bumps.
Inflammation
Tattooing involves puncturing the skin with needles containing pigments, causing injury and triggering inflammation. Nerves in the skin detect this injury and send signals to the brain, resulting in tissue swelling and discomfort ranging from mild to severe pain. Inflammation from tattooing can lead to infections ranging from minor to life-threatening.
Tattoo Reactions
Some individuals may have an adverse reaction to tattoo pigments, causing a painful and itchy rash known as a tattoo reaction. Symptoms typically appear only in the area of the offending stain and include blistering, redness, itching, and swelling. Histologically, this rash consists of clusters of histiocytes and tattoo pigments.

