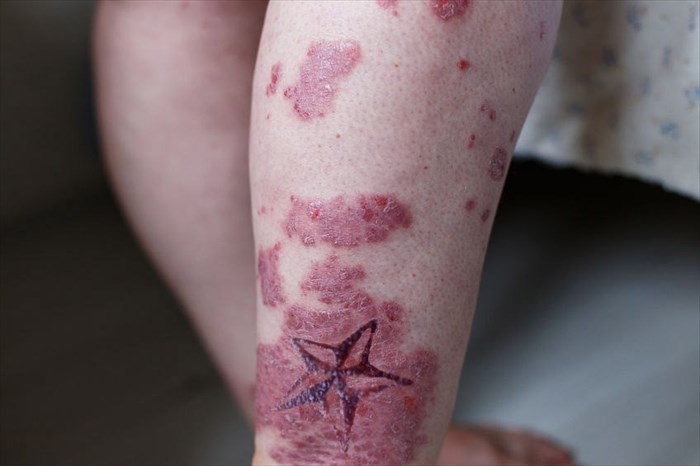
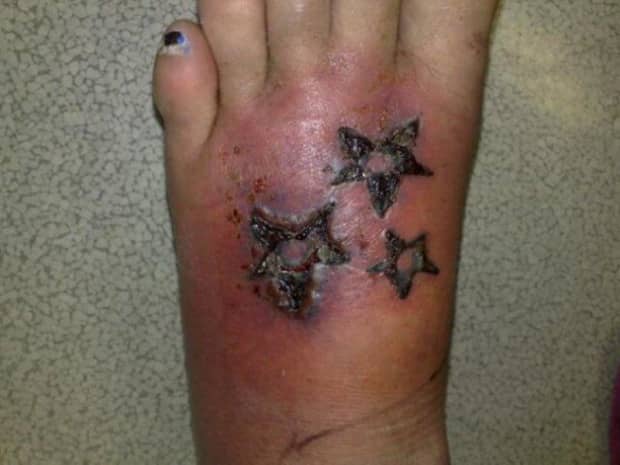
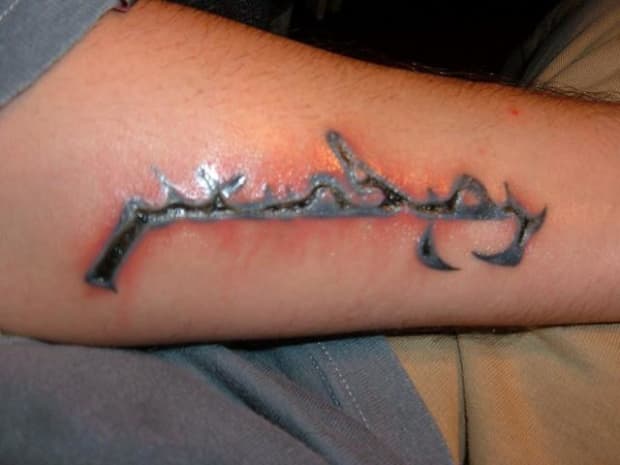
Redness
Redness caused by an infected tattoo is a normal and uncomfortable part of the healing process. It will subside after 24 to 48 hours. Excessive redness and inflammation can be indicative of an allergic reaction to the ink or metals used for your tattoo.
Itching
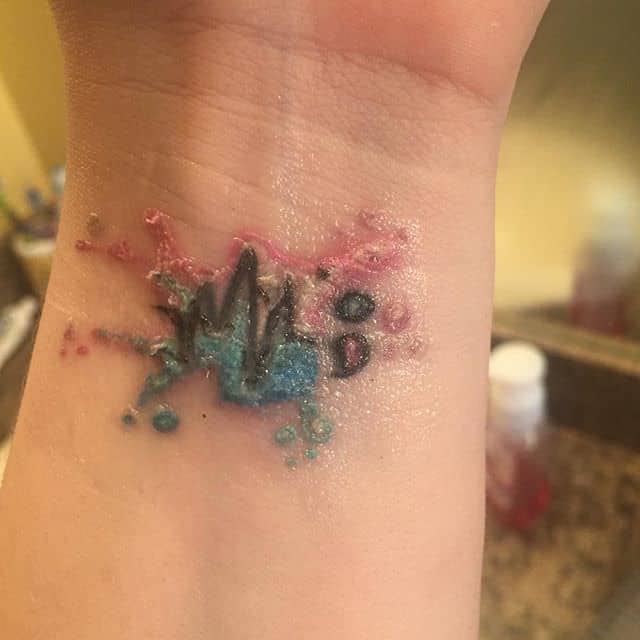
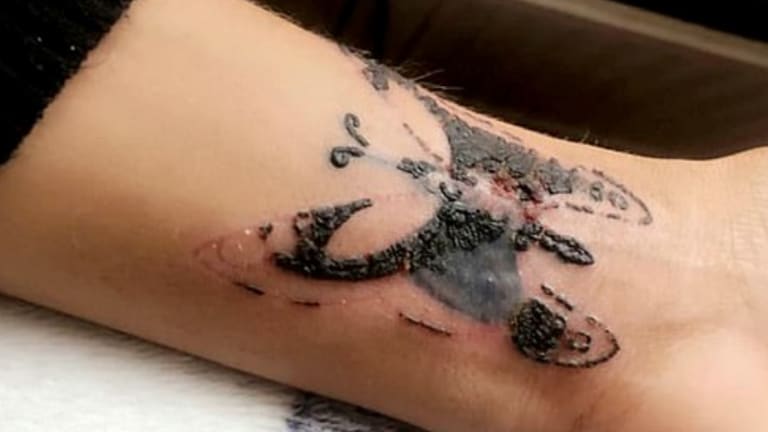

Infected tattoos may cause itching and a rash or red, bumpy skin around the affected area. Itching can be mild initially but if it becomes intense or worsens over time, it’s time to visit a doctor. Taking immunosuppressants under doctor’s guidance can help manage severe itching.
Discharge
After the initial few days, the skin around the tattoo may scab and discharge. This is normal for wound protection. However, if the area continues to ooze and produce yellow or greenish pus, it could be indicative of an infection. Seek medical help if the tattoo oozes excessively or if there are long streaks of redness on the skin.
Ulcers
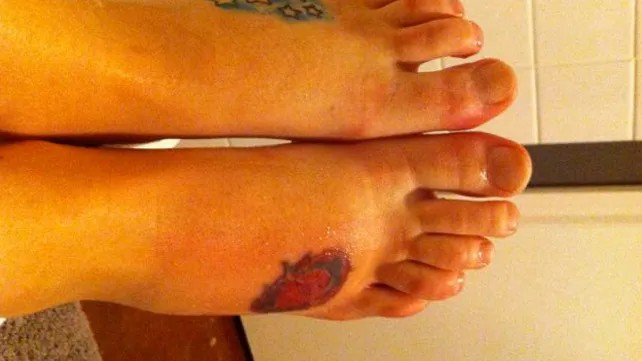
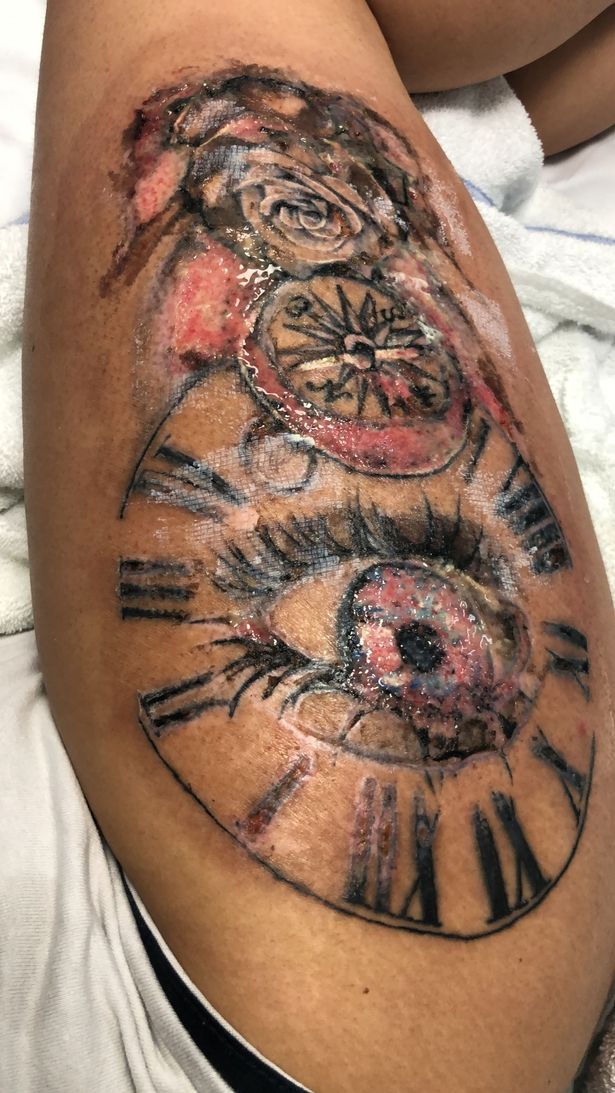

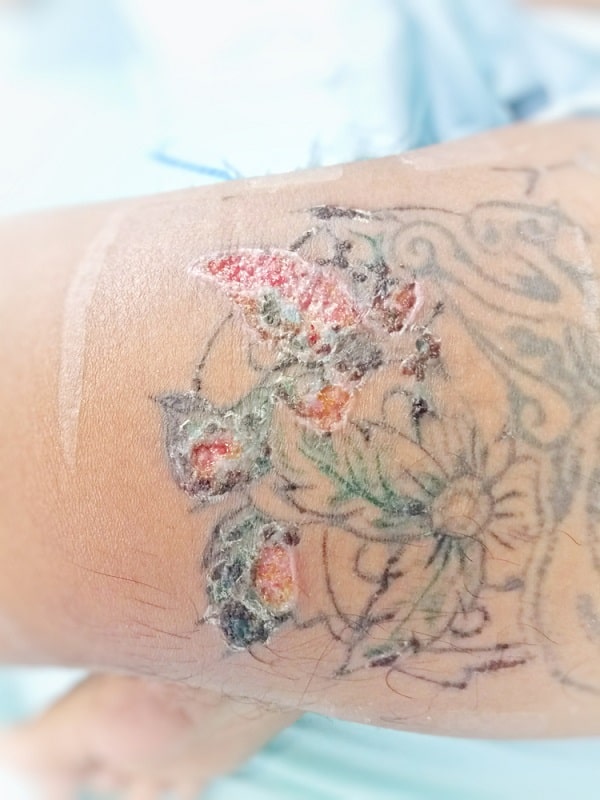
Infected tattoos can develop ulcers and cause pain or inflammation.
Fever
Tenderness and swelling at the tattoo site are common within the first two days. Untreated tattoos can spread bacteria or fungi to other parts of the body, leading to serious infections. Seek medical attention if redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, or discolored streaks continue to worsen.
Treatment
Most tattoo infections can be treated with antibiotics. It’s important to follow medication instructions properly and avoid contact with the skin surrounding the tattoo. In severe cases, hospitalization for IV antibiotics may be required. Samples of skin may be taken to identify the source of infection.

